9. Keras에서 Word2Vec 직접 학습
- 데이터 준비
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import imdb
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = imdb.load_data()- 단어 번호와 단어의 관계를 사전으로 만듦
- 1번은 문장의 시작, 2번은 사전에 없는 단어(OOV)로 미리 지정
word_index = imdb.get_word_index()
index_word = {idx + 3 : word for word, idx in word_index.items()}
index_word[1] = '<START>'
index_word[2] = '<UNKNOWN>'
' '.join(index_word[i] for i in x_train[0])
# 출력 결과
"<START> this film was just brilliant casting location scenery story direction everyone's really
suited the part they played and you could just imagine being there robert redford's is an
amazing actor and now the same being director norman's father came from the same scottish
island as myself so i loved the fact there was a real connection with this film the witty
remarks throughout the film were great it was just brilliant so much that i bought the film
as soon as it was released for retail and would recommend it to everyone to watch and the fly
fishing was amazing really cried at the end it was so sad and you know what they say if you
cry at a film it must have been good and this definitely was also congratulations to the two
little boy's that played the part's of norman and paul they were just brilliant children are
often left out of the praising list i think because the stars that play them all grown up are
such a big profile for the whole film but these children are amazing and should be praised for
what they have done don't you think the whole story was so lovely because it was true and was
someone's life after all that was shared with us all"num_words = max(index_word) + 1
- 텍스트를 단어 번호로 바꾸기
texts = []
for data in x_train:
text = ' '.join(index_word[i] for i in data)
texts.append(text)
len(texts) # 25000- Tokenizer를 사용해 텍스트를 단어로 바꿈
from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
tok = Tokenizer()
tok.fit_on_texts(texts)
new_data = tok.texts_to_sequences(texts)
new_data[0][:10]
# 출력 결과
[28, 11, 19, 13, 41, 526, 968, 1618, 1381, 63]
# 모든 데이터 문장을 토큰화하고 위의 문장을 그 토큰으로 바꾼뒤 10개만 출력
- 단어쌍 만들기
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import make_sampling_table, skipgrams
# 전제 토큰 개수
VOCAB_SIZE = len(tok.word_index)
print(VOCAB_SIZE) # 88581- 단어를 무작위로 추출하면 자주 나오는 단어가 더 많이 나오게 됨
- 이를 방지하기위해 단어를 추출할 확률의 균형을 맞춘 샘플링 표를 생성
table = make_sampling_table(VOCAB_SIZE)- 두 단어씩 뽑아 좌우 2단어(window_size = 2)안에 들어있는 경우가 있는지 없는지 확인하며 데이터 생성
couples, labels = skipgrams(data, VOCAB_SIZE, window_size = 2, sampling_table = table)
couples[:5]
# 출력 결과
[[16876, 497], [9685, 21], [16876, 21917], [383, 5452], [2098, 13577]]- labels에는 윈도우 안에 들어있는 경우가 있으면 1, 없으면 0
labels[:5]
# 출력 결과
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0]- 대상 단어는 word_target으로, 맥락 단어는 word_context로 모음
word_target, word_context = zip(*couples)- 배열로 바꿈
word_target = np.asarray(word_target, dtype = 'int32')
word_context = np.asarray(word_context, dtype = 'int32')
labels = np.asarray(labels, dtype = 'int32')
word_target.shape # (288,)
word_context.shape # (288,)
- skip-gram 모형
- skip-gram 모형은 함수형 API를 사용해야 함
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Activation, Dot, Embedding, Flatten, Input, Reshape
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
def build_model():
input_target = Input(shape = (1, ))
input_context = Input(shape = (1, ))
emb = Embedding(input_dim = VOCAB_SIZE, output_dim = 8)
target = emb(input_target)
context = emb(input_context)
dot = Dot(axes = 2)([target, context])
flatten = Reshape((1, ))(dot)
output = Activation('sigmoid')(flatten)
skipgram = Model(inputs = [input_target, input_context], outputs = output)
return skipgram
model = build_model()
model.summary()
# 출력 결과
Model: "model"
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
==================================================================================================
input_3 (InputLayer) [(None, 1)] 0 []
input_4 (InputLayer) [(None, 1)] 0 []
embedding_5 (Embedding) (None, 1, 8) 708648 ['input_3[0][0]',
'input_4[0][0]']
dot (Dot) (None, 1, 1) 0 ['embedding_5[0][0]',
'embedding_5[1][0]']
reshape (Reshape) (None, 1) 0 ['dot[0][0]']
activation (Activation) (None, 1) 0 ['reshape[0][0]']
==================================================================================================
Total params: 708,648
Trainable params: 708,648
Non-trainable params: 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
- 모델 컴파일 및 학습
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
model.compile(optimizer = Adam(),
loss = 'binary_crossentropy',
metrics = ['accuracy'])
model.fit([word_target, word_context], labels, epochs = 30)
- 임베딩 레이어 저장 및 로드
emb = model.layers[2]
emb.get_weights()
# 출력 결과
[array([[ 0.01938832, 0.01921825, -0.0462908 , ..., 0.01147114,
-0.04764376, 0.01121316],
[-0.01068624, -0.04315212, 0.00839611, ..., -0.02030395,
-0.02321514, -0.03680412],
[ 0.00915837, 0.00973357, 0.00904005, ..., 0.01291057,
0.04295233, 0.0488804 ],
...,
[ 0.01314208, 0.02786795, 0.01130085, ..., 0.03705814,
0.0427903 , 0.0109529 ],
[-0.03585767, -0.04641544, -0.02590518, ..., -0.00451361,
-0.03019956, 0.01893195],
[ 0.00769577, -0.02014879, -0.03623866, ..., -0.03457584,
-0.02138668, 0.02141118]], dtype=float32)]# 임베딩 레이어 저장
np.save('emb.npy', emb.get_weights()[0])- 임베딩 레이어 로드
w = np.load('emb.npy')- 임베딩 레이어를 추가할 때 trainable을 False로 하면 추가학습이 이루어 지지 않음
emb_ff = Embedding(input_dim = num_words, output_dim = 8, input_length = 30,
weights = [w], trainable = False)
10. 사전 훈련된 단어 임베딩 사용하기: GloVe 임베딩
- 원본 IMDB 텍스트 내려받기
import wget
import os
import zipfile
wget.download("http://mng.bz/0tIo")
local_zip = '0tIo'
zip_ref = zipfile.ZipFile(local_zip, 'r')
zip_ref.extractall()
zip_ref.close()
imdb_dir = "aclImdb"
train_dir = os.path.join(imdb_dir, 'train')
labels = []
texts = []
for label_type in ['neg', 'pos']:
dir_name = os.path.join(train_dir, label_type)
for fname in os.listdir(dir_name):
if fname[-4:] == '.txt':
f = open(os.path.join(dir_name, fname), encoding = 'utf-8')
texts.append(f.read())
f.close()
if label_type == 'neg':
labels.append(0)
else:
labels.append(1)
texts[0]
# 출력 결과
"Story of a man who has unnatural feelings for a pig. Starts out with a opening scene that is
a terrific example of absurd comedy. A formal orchestra audience is turned into an insane,
violent mob by the crazy chantings of it's singers. Unfortunately it stays absurd the WHOLE
time with no general narrative eventually making it just too off putting. Even those from the
era should be turned off. The cryptic dialogue would make Shakespeare seem easy to a third grader.
On a technical level it's better than you might think with some good cinematography by future
great Vilmos Zsigmond. Future stars Sally Kirkland and Frederic Forrest can be seen briefly."
labels[0] # 0(부정적인 리뷰)
- 데이터 토큰화
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
max_len = 100
training_samples = 200
validation_samples = 10000
max_words = 10000
tokenizer = Tokenizer(num_words = max_words)
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(texts)
sequences = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(texts)
word_index = tokenizer.word_index
print(len(word_index)) # 88582data = pad_sequences(sequences, maxlen = max_len)
labels = np.asarray(labels)
print(data.shape) # (25000, 100)
print(labels.shape) # (25000,)indices = np.arange(data.shape[0])
np.random.shuffle(indices)
data = data[indices]
labels = labels[indices]
x_train = data[:training_samples]
y_train = labels[:training_samples]
x_val = data[training_samples : training_samples + validation_samples]
y_val = labels[training_samples : training_samples + validation_samples]
print(x_train.shape) # (200, 100)
print(y_train.shape) # (200,)
print(x_val.shape) # (10000, 100)
print(y_val.shape) # (10000,)
- GloVe 단어 임베딩 내려받기
import wget
wget.download("http://nlp.stanford.edu/data/glove.6B.zip")
# 압축풀기
local_zip = 'glove.6B.zip'
zip_ref = zipfile.ZipFile(local_zip, 'r')
zip_ref.extractall()
zip_ref.close()
- 임베딩 전처리
- GloVe 파싱
# 데이터를 라인 단위로 불러오기
glove_dir = "glove.6B"
embeddings_index = {}
f = open(os.path.join(glove_dir, 'glove.6B.100d.txt'), encoding = 'utf8')
for line in f:
values = line.split()
word = values[0]
coefs = np.asarray(values[1:], dtype = 'float32')
embeddings_index[word] = coefs
f.close()
print(len(embeddings_index)) # 400000embedding_dim = 100
embedding_mat = np.zeros((max_words, embedding_dim))
for word, i in word_index.items():
if i < max_words:
embedding_vector = embeddings_index.get(word)
if embedding_vector is not None:
embedding_mat[i] = embedding_vector
embedding_mat
# 출력 결과
array([[ 0. , 0. , 0. , ..., 0. ,
0. , 0. ],
[-0.038194 , -0.24487001, 0.72812003, ..., -0.1459 ,
0.82779998, 0.27061999],
[-0.071953 , 0.23127 , 0.023731 , ..., -0.71894997,
0.86894 , 0.19539 ],
...,
[ 0.13787 , -0.17727 , -0.62436002, ..., 0.35506001,
0.33443999, 0.14436001],
[-0.88968998, 0.55208999, -0.50498998, ..., -0.54351002,
-0.21874 , 0.51186001],
[-0.17381001, -0.037609 , 0.068837 , ..., -0.097167 ,
1.08840001, 0.22676 ]])
- 모델 정의
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding, Flatten, Dense
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(max_words, embedding_dim, input_length = max_len))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(32, activation = 'relu'))
model.add(Dense(1, activation = 'sigmoid'))
model.summary()
# 출력 결과
Model: "sequential_5"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
embedding_7 (Embedding) (None, 100, 100) 1000000
flatten_2 (Flatten) (None, 10000) 0
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 32) 320032
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 1) 33
=================================================================
Total params: 1,320,065
Trainable params: 1,320,065
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________# 가중치 설정
model.layers[0].set_weights([embedding_mat])
# 학습하지 않고 기존의 가중치값 그대로 사용
model.layers[0].trainable = Falsemodel.compile(optimizer = 'rmsprop',
loss = 'binary_crossentropy',
metrics = ['accuracy'])
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
epochs = 10,
batch_size = 32,
validation_data = (x_val, y_val))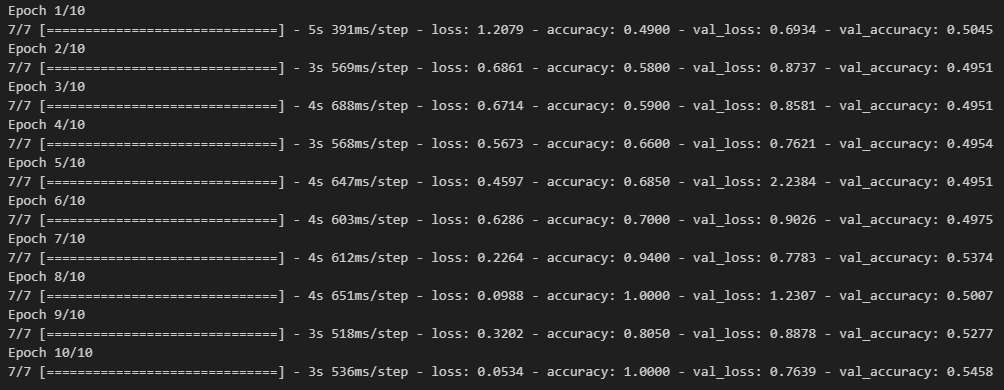
# 모델 저장
model.save_weights('pre_trained_glove_model.h5')
- 시각화
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
acc = history.history['accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy']
epochs = range(1, len(loss) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'b--', label = 'Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'r:', label = 'Validaiton Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'b--', label = 'Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'r:', label = 'Validaiton Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
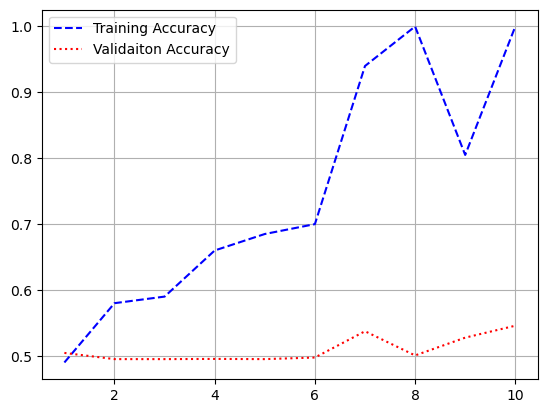
11. 사전 훈련된 단어 임베딩을 사용하지 않고 같은 모델 훈련
model2 = Sequential()
model2.add(Embedding(max_words, embedding_dim, input_length = max_len))
model2.add(Flatten())
model2.add(Dense(32, activation = 'relu'))
model2.add(Dense(1, activation = 'sigmoid'))
model2.summary()
# 출력 결과
Model: "sequential_6"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
embedding_8 (Embedding) (None, 100, 100) 1000000
flatten_3 (Flatten) (None, 10000) 0
dense_4 (Dense) (None, 32) 320032
dense_5 (Dense) (None, 1) 33
=================================================================
Total params: 1,320,065
Trainable params: 1,320,065
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________model2.compile(optimizer = 'rmsprop',
loss = 'binary_crossentropy',
metrics = ['accuracy'])
history2 = model2.fit(x_train, y_train,
epochs = 10,
batch_size = 32,
validation_data = (x_val, y_val))
loss = history2.history['loss']
val_loss = history2.history['val_loss']
acc = history2.history['accuracy']
val_acc = history2.history['val_accuracy']
epochs = range(1, len(loss) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'b--', label = 'Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'r:', label = 'Validaiton Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'b--', label = 'Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'r:', label = 'Validaiton Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()

- 테스트 데이터 토큰화
test_dir = os.path.join(imdb_dir, 'test')
labels = []
texts = []
for label_type in ['neg', 'pos']:
dir_name = os.path.join(test_dir, label_type)
for fname in os.listdir(dir_name):
if fname[-4:] == '.txt':
f = open(os.path.join(dir_name, fname), encoding = 'utf8')
texts.append(f.read())
f.close()
if label_type == 'neg':
labels.append(0)
else:
labels.append(1)
sequences = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(texts)
x_test = pad_sequences(sequences, maxlen = max_len)
y_test = np.asarray(labels)
print(x_test.shape) # (25000, 100)
print(y_test.shape) # (25000,)model.load_weights('pre_trained_glove_model.h5')
model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
# 출력 결과
loss: 0.7546 - accuracy: 0.5566
[0.754594087600708, 0.5565599799156189]'Python > Deep Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [딥러닝-케라스] 케라스 순환신경망(RNN, LSTM, GRU) (0) | 2023.06.03 |
|---|---|
| [딥러닝-케라스] 케라스 텍스트 처리 및 임베딩(1) (0) | 2023.05.17 |
| [딥러닝-케라스] 케라스 전이학습 (1) | 2023.05.17 |
| [딥러닝-케라스] 케라스 CIFAR10 CNN 모델 (0) | 2023.05.16 |
| [딥러닝-케라스] 케라스 Fashion MNIST CNN 모델 (0) | 2023.05.14 |